Cancer Target CtBP
The paralogous transcription coregulators C-terminal Binding Proteins (CtBP) 1 and 2 are critical modulators of numerous cellular processes. CtBP 1 and 2 are overexpressed in many human cancers where they act to inhibit apoptosis and promote metastasis. Unusual among transcription factors, CtBP harbors an essential D-isomer specific 2-hydroxyacid dehydrogenase (D2-HDH) catalytic domain that enables CtBP to be a redox sensor and provides an attractive target for small molecule inhibition. Our collaborator, Dr. Steven Grossman at Virginia Commonwealth University, has shown that high concentrations of substrate are able to inhibit tumor growth in cell culture and mouse studies providing proof-of-principle that CtBP could be an excellent cancer target. We are using structural-based approaches to develop high affinity inhibitors that bind in the substrate pocket (see figure) and can disrupt the oligomeric form required for co-transcriptional activity as potential lead compounds for the development of antineoplastic CtBP inhibitors.
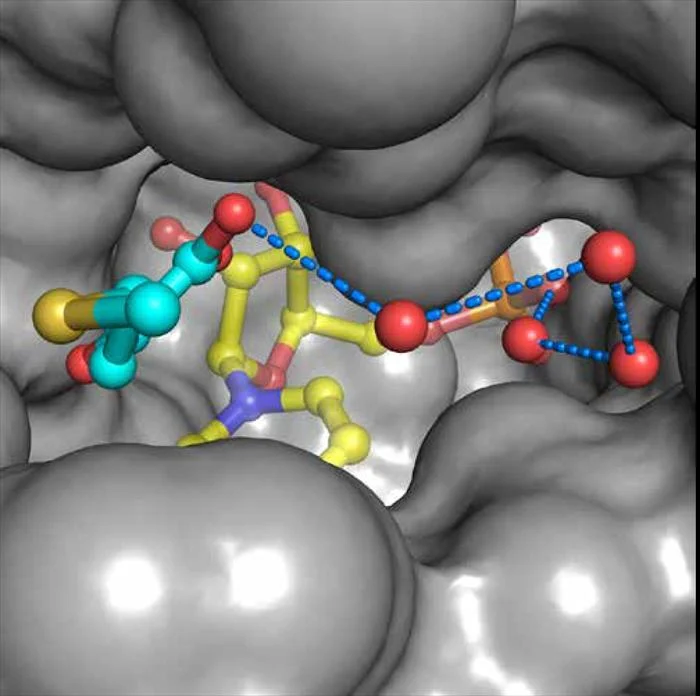
.
The co-transcriptional factor C-terminal Binding Protein (CtBP) has been shown to be up- regulated in a broad range of cancers where it promotes growth and metastasis and inhibits apoptosis. The Royer lab is using structure-based design approaches to develop inhibitors to CtBP that would be useful both as research tools to investigate the role of CtBP in cancer and potentially as lead compounds for antineoplastic therapeutics. Our strongest inhibitor to date was designed to bind in the active site identified in our crystal structures of CtBP (see below). We are using this compound as a scaffold onto which to add additional moieties that may both enhance affinity and biological response. In this project, we use computational modeling software with our CtBP crystal structures to design inhibitors and then synthesize the compounds working with our collaborating medicinal chemist Dr. Akbar Ali. Such compounds will then be tested for binding affinity and, if they bind tightly, used in protein crystallography to delineate precise details of their binding. Favorable compounds identified in this way will then be used by our collaborators to investigate their cellular effects. A laboratory rotation on this project will provide the student with experience in structural biology, computational modeling and/or organic synthesis.”
Binding of HIPP (cyan) in the active site of CtBP1 as revealed by the co-crystal structure (Hilbert et al. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015 10, 1118- 1127). This compound was designed based on our previous crystal structures and binds with a dissociation constant of 370nM, the highest affinity CtBP inhibitor discovered to date. The structure shown suggests that adding moieties to HIPP could provide additional favorable interactions for binding.”
