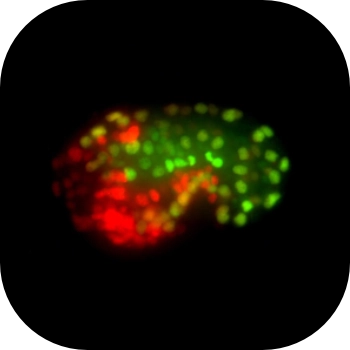
 The mex-3 3' untranslated region is essential for reproduction during temperature stress.
The mex-3 3' untranslated region is essential for reproduction during temperature stress.
Hannah E. Brown, Haik V. Varderesian, Sara A. Keane, Sean P. Ryder
bioRxiv (2024)
 The endogenous mex-3 3' UTR is required for germline repression and contributes to optimal fecundity in C. elegans
The endogenous mex-3 3' UTR is required for germline repression and contributes to optimal fecundity in C. elegans
Albarqi, M.M.Y. and Ryder S.P.
PLOS Genet. (2021) Aug 23;17(8):e1009775. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009775.
x
RNA regulation is essential to successful reproduction. Messenger RNAs delivered from parent to progeny govern early embryonic development. RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) are the key effectors of this process, regulating the translation and stability of parental transcripts to control cell fate specification events prior to zygotic gene activation. The KH-domain RBP MEX-3 is conserved from nematode to human. It was first discovered in Caenorhabditis elegans, where it is essential for anterior cell fate and embryo viability. Here, we show that loss of the endogenous mex-3 3´UTR disrupts its germline expression pattern. An allelic series of 3´UTR deletion variants identify repressing regions of the UTR and demonstrate that repression is not precisely coupled to reproductive success. We also show that several RBPs regulate mex-3 mRNA through its 3´UTR to define its unique germline spatiotemporal expression pattern. Additionally, we find that both poly(A) tail length control and the translation initiation factor IFE-3 contribute to its expression pattern. Together, our results establish the importance of the mex-3 3´UTR to reproductive health and its expression in the germline. Our results suggest that additional mechanisms control MEX-3 function when 3´UTR regulation is compromised.
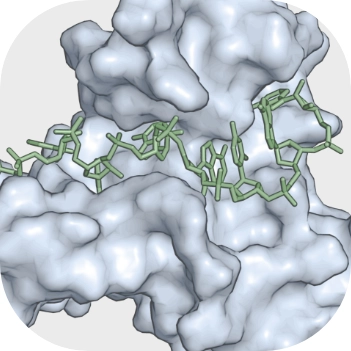 The role of RNA-binding proteins in orchestrating germline development in Caenorhabditis elegans
The role of RNA-binding proteins in orchestrating germline development in Caenorhabditis elegans
Albarqi, M.M.Y. and Ryder, S.P.
Front. Cell. Dev. Biol., (2023) 10:1094295.doi:10.3389/fcell.2022.1094295
RNA passed from parents to progeny controls several aspects of early development. The germline of the free-living nematode Caenorhabditis elegans contains many families of evolutionarily conserved RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) that target the untranslated regions of mRNA transcripts to regulate their translation and stability. In this review, we summarize what is known about the binding specificity of C. elegans germline RNA-binding proteins and the mechanisms of mRNA regulation that contribute to their function. We examine the emerging role of miRNAs in translational regulation of germline and embryo development. We also provide an overview of current technology that can be used to address the gaps in our understanding of RBP regulation of mRNAs. Finally, we present a hypothetical model wherein multiple 3′UTR-mediated regulatory processes contribute to pattern formation in the germline to ensure the proper and timely localization of germline proteins and thus a functional reproductive system.
