APOBEC Inhibitors
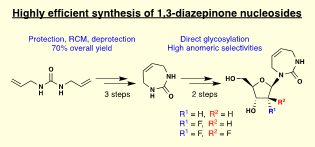
The APOBEC3 family of enzymes catalyzes the deamination of cytosine (C) to uracil (U) in single-stranded DNA substrates. These enzymes play an important role in innate immunity, but when misregulated cause somatic mutations to the human genome that lead to cancer evolution and drug resistance. Therefore, there is significant interest in developing inhibitors of APOBEC3 enzymes as potential therapeutics. Recent biochemical and structural data has shown that nucleoside-based cytidine deaminase (CDA) inhibitors can also inhibit APOBEC3 enzymes when incorporated into short oligonucleotides. We are interested in developing efficient synthetic routes to modified nucleosides, especially CDA inhibitors, and incorporating these into oligonucleotides to target APOBEC3 enzymes. Recently, we developed efficient convergent routes to multiple 2′-modified-diazepinone nucleosides. These potent CDA inhibitors are key synthetic intermediates required to synthesize diazepinone-containing oligonucleotides as potential APOBEC3 inhibitors. We are working with the Watts lab (RTI) to incorporate diverse CDA inhibitors into short oligonucleotides for evaluation as potential APOBEC3 inhibitors.
Relevant Publications:
Hedger, A. K.; Findell, J.; Barak, D. S.; Schiffer, C. A.; Watts, J. K.; Ali, A. Efficient Convergent Synthesis of 1,3-Diazepinone Nucleosides by Ring-Closing Metathesis and Direct Glycosylation. RSC Advances, 2024, 14 (50), 37216–37226.
